Solanaceae
(Also known as Black nightsade family/Potato family)
i. Distribution
Cosmopolitan in distribution, abundant in tropical to temperate regions of the world.
ii. Habit and Habitat
Usually annual or perennial herbs, shrubs and rarely trees and climbers; mostly mesophytes, rarely xerophytes (solanum xanthocarpum); wild or cultivated
Vegetative characters
i. Root
Taproot and branched
ii.Stem
Erect, mostly herbaceous, solid or fistular, cylindrical, branched, glabrous or pubescent, sometimes spiny or prickly; sometimes modified into underground tuber (solanum tuberosum).
iii.Leaf
Cauline and Ramal, alternate or opposite, exstipulate, petiolate, usually simple, rarely compound, margin entire or dentate or hairy; unicostate reticulate venation
Floral characters
i.Inflorescence
Usually cymose; sometimes solitary (terminal or axillary)
ii.Flower
Ebracteate, Ebracteolate, pedicillate, bisexual, rarely unisexual (Withaniab somnifera), complete, Actinomorphic, sometimes zygomorphic (Schixanthus), pentamerous, hypogynous
iii. Calyx
Sepals 5, gamosepalous, five-lobed or toothed, persistent, valvate or imbricate aestivation, pubescent, inferior
iv.Corolla
Petals 5, gamopetalous, infundibuliform or campanulate or tubular etc, twisted or valvate aestivation
v. Androecium
Stamens 5, polyandrous, epipetalous, alternipetalous, anther dithecous, basifixed or dorsifixed, introrse, inferior
vi. Gynoecium
Bicarpellary, syncarpous, bilocular, sometimes tetralocular due to the formation of false septum; placenta swollen, ovules many, axile placentation, ovary superior and obliquely placed
vii.Fruit
Berry or capsule
Pollination: Self or cross
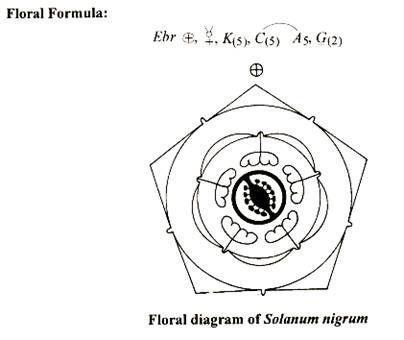
Floral Formula of Solanaceae
Ebr.⊕⚥K(₅)C(₅)A₅G̲(₂)
Explanation:
- ⚥ → Bisexual flower (contains both stamens and carpels)
- ⊕ → Actinomorphic (radially symmetrical)
- K(5) → Five fused sepals (gamosepalous)
- C(5) → Five fused petals (gamopetalous)
- A5 → Five stamens
- G̲(2) → Bicarpellary, syncarpous superior ovary (underline indicates a superior ovary)